Employees are the most vital resource to a company and have a direct impact on its success. Many executives strive to attract and develop top talent to help meet their short and long-term goals. But in an environment where consumer preferences are constantly evolving, and the need for up to date skills are necessary for success, companies require a means to upskill their workforces in order for them to maintain current. But how can this be achieved if employees are not energized to participate in their own development, or do not recognize the value in it?
To facilitate meaningful employee development programs, companies need to redefine what engagement means in their employee development space.
How will they do this? By prioritizing variety, relevance, and support. Presenting employees with multiple ways to access information and test their understanding will allow them to engage with information in ways that cater to their unique learning styles. Increased support within learning management system softwares will help employees ascertain preferred methods of digesting new information in order to successfully utilize their new skills. As employees experience more fulfillment in their own development, companies will experience the benefit of having workforces that are more eager to acquire new skills relevant for their jobs.
This post articulates recommendations on how to improve engagement in professional development programs through the use of learning management system software. It provides examples on how to make professional development programs more engaging, as well as key strategies which include ensuring content accessibility through multiple modalities, fostering support through AI chatbots and community features, and incorporating personalized learning paths.
The content below emphasizes the value of simulations, role-playing, and gamification to make training interactive and relevant to real-world scenarios. This post also underscores the role of immediate feedback and continuous updates to maintain an engaging learning environment, and enhance professional development programs. As a final point, focusing on improving engagement in professional development programs can help workforces acquire skills more effectively, and make better contributions towards organizational growth.
Methodology
The evaluation of learning management system software began with conducting extensive market research on various learning management system software, and comprehensive literature reviews of best practices for leveraging learning management systems.
To gain further insights, both Human Resource managers and new hires were interviewed to understand how they used learning management system software in their workplaces, for tasks ranging from onboarding processes to daily operations and professional development programs.
1. Content Accessibility
When asked about their experiences using learning management system software during their onboarding processes, new hires communicated that content within LMS software should be easier to identify, so that employees using the platforms can readily locate specific information and features. Better content accessibility could be achieved by providing information to employees through multiple learning modalities such as text, audio, video, or interpersonal activities. It could also be achieved via features that enable ease of navigation within a learning management system software.
Multiple learning modalities will allow employees to digest information in ways that cater to their unique learning styles. In learning management system software that contains a multitude of functions, features that allow users to easily navigate through the complexity of the software can help make using it less frustrating. While these are two different ways to think about content accessibility within learning management system softwares, both are equally important for users.
2. Customizable Learning Paths
Customizable learning paths can help you access content that best suits your learning needs and styles. This can be achieved through several means.
Personalized Assessments
Employees can specify their specific goals when starting a skill development program. Assessments can then adapt to the learning paths and skill development goals of the employee.
Skill Based Assessments
Skills for development can be associated with specific roles within a company. Assessments for specific skills can be developed in relation to these roles.
Personalization and Adaptive Learning
Personalization of gamification elements can help support the unique learning styles of employees.
“Personalized learning makes it easier for learners to discover the content they need to build the right skills at the right time. In turn, this will help align your workforce’s desired career paths with organizational goals—helping everyone succeed.” Having the option to customize learning paths gives employees the variety they need to chart a meaningful development path. Let’s dig deeper into the significance of gamification. https://learning.linkedin.com/resources/learner-engagement/how-personalized-learning-enhances-employee-development.

3. Gamification Elements
The article “Does Gamified Training Get Results?” from Harvard Business Review studied the impact of gamification in corporate trainings. The study, conducted at KPMG, showed that when gamified training is correctly implemented, it can enhance employee performance.
The use of gamification as a means to generate better engagement and thus performance surfaced through both my market research and interviews with new hires. Upon synthesizing findings, here are several key suggestions for effectively implementing gamification.

Quests and Challenges
Employees can complete specific modules to unlock new content and rewards. For example, a quest might involve finishing several modules on financial management to unlock advanced techniques. Such components create a sense of adventure and achievement.
Points System
A point system can be incorporated for employees to earn points after completing modules, participating in discussions, or achieving high scores on quizzes. This system incentivizes continuous participation and engagement.
Storytelling and Narrative
A narrative or storyline could be applied where employees progress through a series of chapters or episodes. For example, employees might follow a storyline about a company’s journey to success while completing related training modules. This makes the learning experience more immersive and relatable. It also helps employees connect with the content on a deeper level.
Virtual Rewards
Customizable features for avatars, virtual currency, or other digital items are examples of virtual rewards that employees can collect upon completing specific tasks. For instance, employees might earn virtual currency to customize avatars or unlock special content. This provides additional motivation by allowing employees to express their achievements in a personalized and fun way.
Character Progression
Employees could create characters that progressively develop as they complete training modules and assessments. For instance, a character may begin as a “Novice Learner” and develop into an “Expert Strategist” as they develop more skills through leadership training courses.
4. Simulations and Role-Playing
Consider the example of an electrician who is currently completing an apprenticeship. As they complete classes to hone their craft, they are continuously applying their skills on projects under the guidance of an experienced supervisor. Undoubtedly, this form of experiential learning, while they are taking classes, is needed for journeymen to learn how to correctly apply their skills before they complete their apprenticeship and obtain their electrical contractor license. The same applies to employees. Skill development programs without experiential learning components will not allow for opportunities to bridge the gap between conceptual understanding and practical application.
The importance of simulation learning within professional development programs is also evidenced by the growth in the medical simulation market. While all four categories of simulation training are expected to grow over the next decade, web-based simulations are predicted to be the largest product category within this market. https://market.us/report/medical-simulation-market/
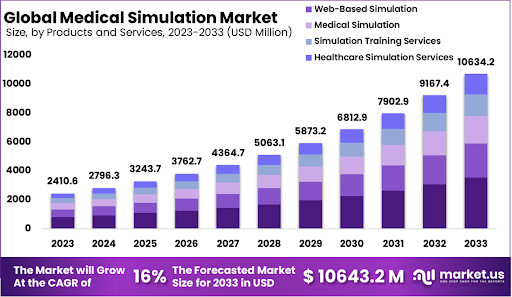
Simulations and role-playing exercises provide opportunities for employees to apply concepts to real life situations, and test the limits of their understanding. Such exercises can also serve as informal assessments so that employees can understand what skills need to be improved. What additional components can we leverage to integrate experiential learning for employees?
5. Interactive Case Studies
Improved Decision-Making Skills
Scenarios with multiple decision points allow employees to explore different outcomes based on their choices, helping them understand the consequences of various actions. This enhances their strategic thinking and decision-making skills.
Preparation for Dynamic Challenges
Including hypothetical scenarios that show altered realities based on different decisions prepares employees for the dynamic nature of real-world challenges. Employees can become more adaptable and better equipped to handle unexpected situations.
Understanding Long-Term Impacts
Interactive case studies can highlight the long-term impacts of different decisions. This can help employees consider the broader implications of their actions. This holistic approach to decision-making encourages employees to think beyond immediate outcomes, fostering a deeper understanding of strategic planning and risk management.
Simulations, role-playing, and interactive case studies adequately provide employees with the experiential learning they need to apply their skills to the workplace.
6. Real-World Relevance
Real-world scenarios support employees in their reflection of actual workplace challenges. By seeing the immediate value of their training, employees can become more engaged and motivated. Simulations and scenarios that mimic real-world situations provide learners with a risk-free environment to practice and refine their skills, and enhance their problem-solving abilities. This can boost confidence when certain challenges in the workplace arise. Skills and knowledge acquired during trainings can be directly applicable to the specific roles, and help facilitate smoother transitions from learning to implementation.
Additionally, when employees engage with realistic problems and scenarios during their trainings, they develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills that can be transferred to their roles. Professional development programs that reflect current industry trends and practices ensure that employees maintain a competitive and proficient skill set within their fields. Such developments in individual performance can improve their contributions to the overall organization. Organizations can better prepare their workforce to meet current and future challenges by making professional development programs relevant and practical.
7. Support and Community

Support within a learning management system software encompasses resources and assistance that supports employees in effectively using the system to achieve their professional development goals. What might these resources and supports look like?
AI Chat Bots
Can provide quick answers for common technical questions and step-by-step guidelines for accessing features. They can also provide guidelines for language accessibility and support bilingual employees, and employees with disabilities.
Mentorship Coaching
Features that allow employees to collaborate with company mentors can provide easy access to support and community while progressing through training. Sharing of analytics and other information from training can be facilitated through these interactions.
Engagement Platforms
Chat rooms, message boards, and virtual communities allow employees to engage in conversations about learning experiences and topics of interest. This facilitates a sense of collective learning amongst employees.
Content Sharing
Senior employees can generate content that can be accessible to other employees in professional development programs. This allows them to leverage their expertise in the company for the benefit of others.
Support mechanisms and community interactions lay the framework for a strong and connected learning environment. There is also value in the social interactions and collaborations that emerge from this.
8. Social Interaction and Collaboration
This is a powerful attribute that was communicated by both new hires and HR managers as being simultaneously very important and underused within professional development programs. Social interaction and collaboration that is integrated into professional development programs can help foster a culture of collective and collaborative learning. Features such as team challenges, group projects, and peer-to-peer learning can encourage employees to support each other through various elements of professional development programs. Social interactions through discussion forums, chat functionalities, and social media integration can also aid in the dissemination of information in moments of difficulty. Additionally, peer-to-peer mentorship can easily be facilitated through such features to increase support for employees.
Creating a sense of oneness amongst employees through professional development programs can increase engagement and help develop a sense of cohesion as the company addresses new challenges.
9. Immediate Feedback and Performance Analytics
Feedback loops are part of a system in which some portion of the system’s outputs are used as inputs for future operations. The following process outlines the creation of a feedback loop. Feedback is initially collected through surveys, app feedback forms, or through communication with employees. The feedback is then analyzed for patterns. This helps develop an understanding of positive and negative user experiences. Once conclusive findings are developed from the analysis, they are then executed into actionable steps that are integrated into the system for improvement. https://www.techtarget.com/searchitchannel/definition/feedback-loop
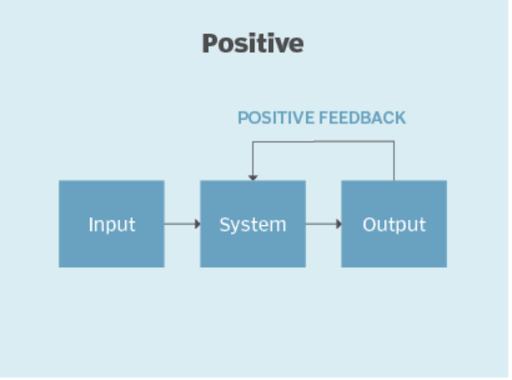
Gathering user feedback is essential for identifying best practices, and areas for improvement in learning management system software. Feedback loops can provide information on how learning management system software can best meet the personalized needs of employees to provide an effective learning experience. Seeing feedback being implemented can foster more engagement, and incentivize employees to take more ownership over their professional development. Regularly collecting and acting on feedback helps identify and address pain points, and enhance user satisfaction and retention. This iterative process of improvement keeps the learning management system software aligned with the learners’ evolving preferences and needs.
By understanding user behavior and preferences, companies can also modify the content and delivery methods in their learning management system software to maximize engagement and learning outcomes. Data-driven approaches ensure that the LMS remains relevant and effective. As employees continuously interact with LMS systems that adapt to their feedback, they are more likely to remain committed to their learning paths. This sustained engagement is crucial for successful up-skilling initiatives, and driving organizational growth. More so, these mechanics of feedback loops form the foundation for continuous improvement in how the LMS system can make training more engaging.
10. Continuous Improvement and Updates
Continuous improvements and updates of components of learning management system software designed to increase engagement can energize employees as they acquire relevant skills in a professional atmosphere where new skill demands frequently emerge. Regular updates ensure that content remains relevant and aligned with current industry trends, technologies, and best practices. This can enhance the overall user experience. By incorporating the latest features and addressing security vulnerabilities, the LMS stays robust and reliable and supports a seamless learning environment.
Gamified elements in a LMS need regular updates in order to present content that is up-to-date and engaging. Continuous enhancement of these elements based on the latest trends in gamification can significantly boost learner motivation and participation. By integrating innovative features and maintaining an interactive learning atmosphere, the LMS can sustain interest and encourage ongoing skill development.
Conclusion
Engaging training within learning management system software are essential for professional development because they significantly enhance motivation, retention, and application of skills. More so, the long term benefits of improving professional development experiences will be recognized through company performance. To take your employee development programs to the next level, start leveraging the components of your company’s LMS that spotlight engagement today to help your workforce progress towards their skill goals.
Sources Cited
- LinkedIn Learning. “How Personalized Learning Enhances Employee Development.” LinkedIn Learning, https://learning.linkedin.com/resources/learner-engagement/how-personalized-learning-enhances-employee-development. Accessed 18 July 2024.
- Rouse, Margaret. “Feedback Loop.” TechTarget, TechTarget, 14 June 2023, https://www.techtarget.com/searchitchannel/definition/feedback-loop. Accessed 18 July 2024.
- Bersin, Josh, and Marc Zao-Sanders. “Does Gamified Training Get Results?” Harvard Business Review, Harvard Business Publishing, 14 Mar. 2023, https://hbr.org/2023/03/does-gamified-training-get-results. Accessed 18 July 2024.
- “Medical Simulation Market Size, Trends, Growth, Analysis, Demand, Opportunities and Forecast 2023 to 2032.” Market.us, Market.us, 2023, https://market.us/report/medical-simulation-market/. Accessed 18 July 2024.



