The dynamics of work and team management have undergone a sea-change. Situational leadership has produced overwhelming results.
Organizations comprise employees coming from diverse backgrounds and environments. It becomes an arduous task for managers to handle such a heterogeneous workforce.
Managers feel that a single style of leadership is not practical. They believe in the situational leadership model. With an ever-changing and volatile business environment, leaders must adopt a responsive leadership style.
What is Situational Leadership?
Situational Leadership means that leaders adapt their leadership style according to the circumstances. Different leadership approaches should be used in different situations to produce the best results.
A leader or a manager has to direct and lead a team that comprises members from or having different:
- Backgrounds
- Level of education
- Experience
- Personality
- Skills
- Learning style
- Desires that act as motivators
A great leader is aware of these differences. Nowadays, managers understand their employees and use different leadership approaches to direct them. They bring out the best in their employees by using a participating style of leadership.
Situational Leadership Theory
The situational approach to leadership states that managers should be flexible in their leadership styles. They should modify their leadership style to meet the needs of the employees as well as the organization.
Employees have different levels of competence and expertise. The complexity of the task also affects the style of leadership. Some assignments are mundane and of routine nature, while some others are complicated and require close supervision. A manager should take into account all these factors while leading a team.
Different situations need different leadership approaches. For example, if an employee is new, the manager should infuse confidence in him. Since the employee doesn’t know much about the work processes, it would be better if the manager guides and helps him.
On the other hand, managers can give greater autonomy to experienced employees. Such employees do not require much guidance and hand-holding.
Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory
Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard have given a model of situational leadership that organizations now use widely. Their situational leadership model states that leadership approaches should be task-relevant. Their model outlines two main concepts:
- The styles of leadership
- The development or maturity level of the employees
Styles of Leadership
Hersey and Blanchard have divided the leadership styles into four categories based on task and relationship behavior. The four styles are as follows:
S1 or Telling
This leadership style should be adopted by the managers when the employees do not have the required skill. This style states that the leader should work in close collaboration with the employees.
The employees are novices. Their level of competence is low, but they are willing to learn and show enthusiasm towards their work. The managers need to tell such employees all the details about the task. They should direct and guide them constantly.
Managers should demonstrate to them the working of the task. As the employees are not skilled and they lack the expertise, managers should instruct them.
S2 or Selling
Managers should adopt situational management and leadership when the employees have some competence regarding their work but are unwilling to contribute 100 percent. In the selling style, the leaders persuade the employees to give their best.
They have to motivate the employees and create a sense of belonging towards the organization. Managers can use different strategies to motivate the employees, like giving them monetary and non-monetary incentives.
The leaders should boost their morale and uplift the employees’ spirits. They should value the employees’ contribution and make them feel important; such an approach encourages them to perform better.
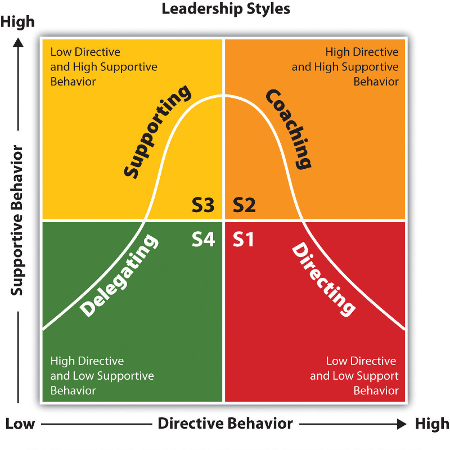
S3 or Participating
The participating style of leadership is helpful in the circumstances when the employees possess the knowledge but lack confidence. If the managers involve the employees in the decision-making process, they would feel more confident.
The leaders should use a participating leadership style to infuse self-belief among the employees. If the employees have the skills and experience, the leaders should enhance them. They should allow them to make decisions in their area of expertise.
Situational leaders take suggestions from the employees and work as a team. Employee engagement plays a vital role in the success of the organization. Democratic leaders should not dictate their employees and instead collaborate with them for outstanding results.
S4 or Delegating
The fourth situational leadership style is Delegating. Leaders use this style when the employees are capable and willing to do their tasks.
Employees possess the insight, skills, and confidence to accomplish their objectives. They also have the desired experience and are eager to take responsibility for the work.
In such a scenario, managers should delegate the work to the employees and make them accountable for the results. A leader using this leadership style should:
- Have a clear vision
- State the objectives with clarity
- Give authority along with responsibility
The employees are competent and self-motivated. Hence, they deliver exceptional results when given the freedom to act. Managers should delegate the work to the employees and allow them to work freely within the organization’s rules.
Maturity Level of the Employees
Another crucial consideration in the situational leadership model of Hersey and Blanchard is the maturity level of the employees. The situational approach to leadership says that the leadership style also depends on the team’s maturity level.
Hershey and Blanchard have categorized the maturity level as follows:
M1 or High Level of Maturity:
Employees with a high level of maturity are competent and experienced. They are masters in their field and have the capability to excel.
Such employees are committed to their job and are full of enthusiasm. Highly developed and mature employees are willing to do their work and contribute towards the organizational goals.
M2 or Medium Level of Maturity:
The employees in this category are confident and eager but lack the skill to do the work. They can perform well if the leader trains them and directs them effectively.
The leaders can utilize their willingness by making them able enough to perform the task. They can show them how to do the job and lead by example.
M3 or Medium Level of Maturity:
Employees who are capable but lack the zeal to perform come under this category. They are not motivated to work to the best of their capabilities. They have the expertise, and hence, they can be assets if the manager can motivate them.
Managers should use a participating leadership style to involve them in the job. Managers should develop a sense of ownership in them so that they perform with dedication.
M4 or Low Level of Maturity:
Employees with a low level of maturity do not possess the skill to do the work. They are inexperienced and new to the organization. They are insecure about their work.
Managers need to lead them by giving them clear instructions. They need extreme monitoring and assistance from their leaders.
Situational leadership emphasizes that managers should not restrict themselves to a single style of leadership. They should apply different leadership approaches in different situations. They have to adapt to the changes in the business environment and lead accordingly.
Different leadership approaches give better results. Since the employees needing guidance are not the same, the leadership styles should also vary. Employees, as well as managers, prefer the participating style of leadership as it delivers remarkable results.
Situational Leadership Examples
Scenario 1
Suppose a small organization has received a huge order. The manager has to ensure that the order meets the deadline and is delivered on time. In such a scenario, the production process will involve all the employees, i.e., members from different departments. The manager should encourage the employees to contribute their best.
Some of them may be inexperienced and not know the intricacies of the work. For such team members, the manager should adopt the telling leadership style. The manager must supervise closely and direct them on how to achieve precision in output.
The employees of the Production department who know the work and are committed towards it should help the others. The manager should adopt a participating style of leadership for them and involve them in teaching others.
Scenario 2
A leader should use a delegating style of situational leadership when the employees are capable and committed. The manager should give autonomy to the team. Team members will perform better if they have the authority to make decisions. Authority and responsibility go hand-in-hand. The leader should hold the team responsible for the outcome.
Real-Life Examples
Ratan Tata: Tata Group of Companies
The honorable chairman of the Tata Group of Companies, Mr. Ratan Tata, is known for his selling and participating leadership styles. He motivates his employees to excel and render miraculous results. Along with that, he also seeks inputs from them before implementing a decision.
Mr. Tata’s democratic style of leadership has led to the success of the Tata Group. The employees of the company are satisfied and work with devotion.
Warren Buffet: Berkshire Hathaway
Warren Buffet adopts the delegating style of situational leadership. The employees of his company possess the expertise and competence to perform their job. They are skilled and self-sufficient.
Warren Buffet delegates the task to the employees and trusts them to put in their best. If an employee makes a mistake, he treats it as a learning experience.

Advantages of Situational Leadership
Situational leadership has the following benefits:
Flexible Approach
The situational style of leadership has the flexibility to change. Managers are responsive to the developments happening around them. Situational leaders evaluate the scenario and lead according to it. They adapt their leadership style according to the circumstances.
Each individual has their desires, perspectives, strengths, weaknesses, and expectations. The leader identifies and acknowledges these differences and guides differently for optimum results.
Considers Different Readiness Levels
Situational leadership style takes into account the different readiness levels of employees. It is important to realize that the employees have different maturity levels.
Some employees are more competent, whereas some are less. A few are highly energetic and motivated, while some are not. Hence, a manager should not use the same barometer for them. A manager should apply different leadership approaches to employees with skills and experiences.
Increases Awareness of Leaders
Situational leaders are aware of the changes happening around them, are more empathetic, and understand their employees. Such managers put their employees in suitable positions and lead them.
Delivers Outstanding Results
The situational style of leadership is immensely effective and is the need of the hour. As the business environment is rapidly changing, leaders must accommodate these changes and lead their teams.
Disadvantages of Situational Leadership
The situational approach of leadership is not without its cons.
Creates Confusion
The situational leadership model might result in chaos and confusion in an organization. If a manager can not implement the model and keeps constantly changing their style, it may create havoc.
Short-term Orientation
Situational leadership emphasizes more on short-term developments. Leaders keep in mind the changes happening in the environment and meet the current needs.
This approach is not future-oriented. It tends to overlook the broader perspective and long-term goals of the organization.
Based on Leader’s Ability
The success of situational leadership rests on the ability and sharp insight of the leader. If the leader is not adept and clever, situational leadership might not produce the desired results.
Final Thoughts
Situational leadership is the panacea for all the challenges faced by leaders in organizations. Managers find it difficult to lead today’s increasingly complex and varied workforce. The unpredictable and competitive business environment adds further to the challenge.
Managers must practice situational leadership to lead employees effectively and take their organization to the zenith.





